SCA Awareness
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA)
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a condition in which the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. If this happens, blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs. SCA usually causes death if it's not treated within minutes.
(National Institute of Health)
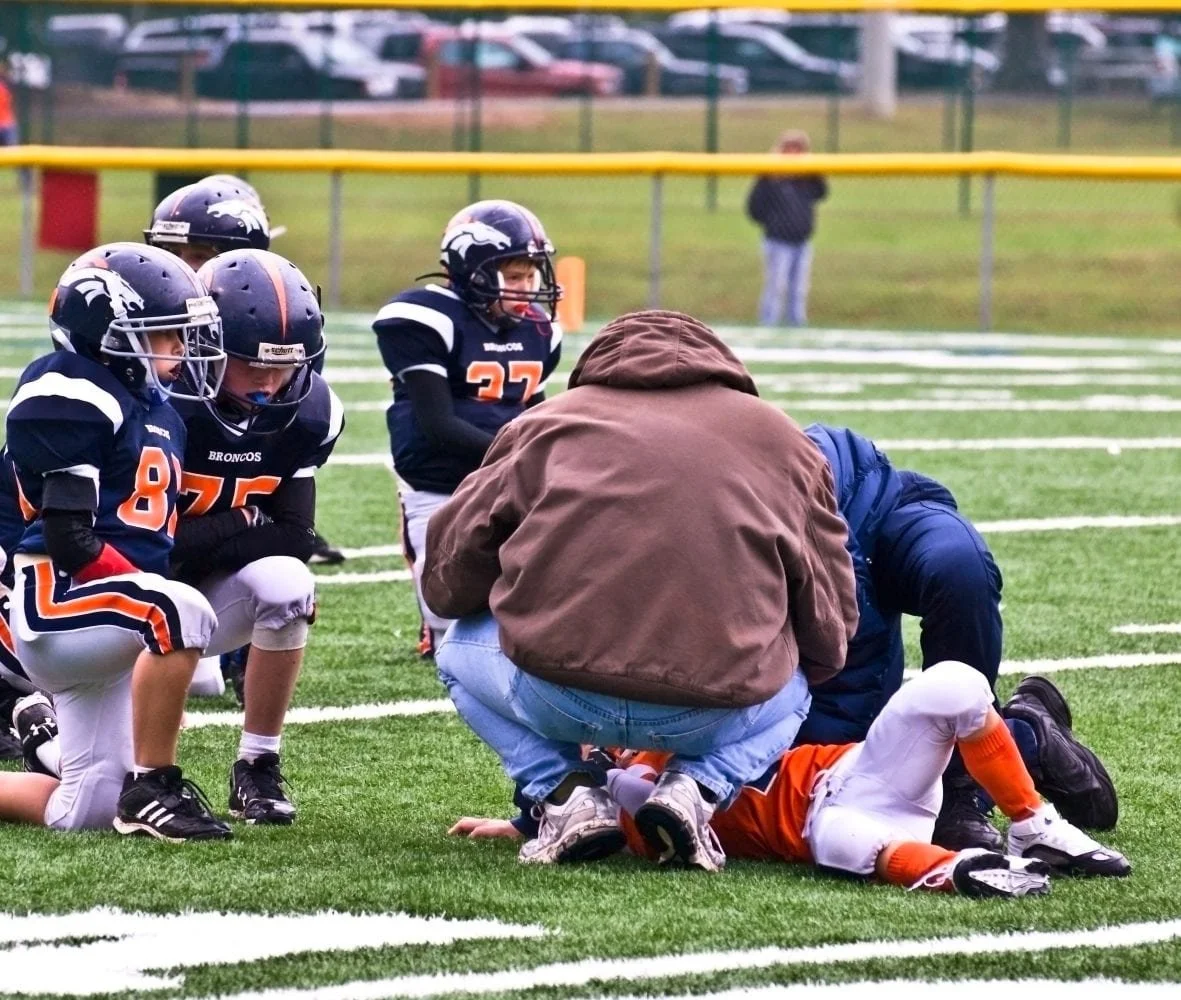
SCA strikes people of all ages who may seem to be healthy, even children and teens.
When SCA happens, the person collapses and doesn’t respond or breathe normally. They may gasp or shake as if having a seizure.
There are more than 436,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests annually in the U.S., nearly 90% of them fatal.
(American Heart Association’s Heart & Stroke Statistics 2020)
Up to 23,000 youth are affected by SCA annually in the US.
A student dies every hour, every day from SCA
#1 killer of student athletes
#2 medical cause of death in youth under 25
Leading cause of death on school campuses
1 in 300 youth has a heart condition that puts them at risk for sudden cardiac death
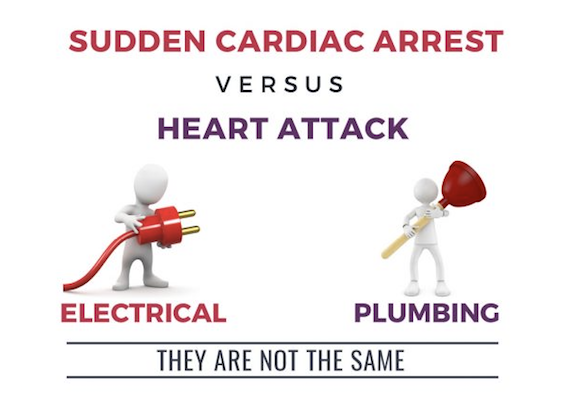
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is not the same as a Heart Attack
-
An electrical malfunction that causes the heart to suddenly and unexpectedly stop beating.
-
Blockage in coronary arteries that interrupts blood flow to the heart.
“The underlying cause of SCA can be a heart condition you’re born with (often inherited) and/or can develop as young hearts grow. SCA can also be triggered from a viral illness, or a blow to the chest from an object or a person. Up to 95% of SCA victims die because there was a delay in emergency response.” ”
Every minute matters
Quick bystander intervention can mean the difference of life or death.
Cardiac Chain of Survival
Recognize Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Call 9-1-1 and onsite first responders immediately
Start CPR immediately—Push hard and push fast on the center of the chest
Use the nearest AED (defibrillator) to restore the heart to its normal rhythm
Direct EMS personnel to the victim